Flutter Basic
플러터가 Dart 를 사용하는 이유
플러터가 Dart 를 사용하는 이유에 대해서 잘 정리된 글에도 나와있고 책에도 나와있듯이 다트가 JIT 컴파일, AOT 컴파일 모두를 지원하기 때문이다.
플러터의 장점(= 리액트 네이티브와 비교하여)
책에서는 ‘자체 렌더링 엔진을 탑재하고 있고, 바로 ARM 코드로 컴파일 한다.’는 장점 덕분에 ‘앱이 네이티브로 구동’되며 리액트 네이티브처럼 자바 스크립트 브릿지와 같은 중간 계층이 필요가 없다고 하고 있다.
공식문서에서 설명하고 있는 아키텍처에서 이와 관련된 여러 내용들을 확인할 수 있는데 몇몇 표현만 봐도 같은 맥락에서 설명하고 있다.
Flutter is a cross-platform UI toolkit that is designed to allow code reuse across operating systems such as iOS and Android, while also allowing applications to interface directly with underlying platform services.
During development, Flutter apps run in a VM that offers stateful hot reload of changes without needing a full recompile. For release, Flutter apps are compiled directly to machine code, whether Intel x64 or ARM instructions, or to JavaScript if targeting the web.
To the underlying operating system, Flutter applications are packaged in the same way as any other native application. A platform-specific embedder provides an entrypoint; coordinates with the underlying operating system for access to services like rendering surfaces, accessibility, and input; and manages the message event loop.
전체적으로 한 마디로 요약하자면 플러터는 어느 플랫폼이든 해당 플랫폼에서 동작하는 native application 처럼 패키징되고 해당 플랫폼의 서비스들과 직접적으로 맞닿아 동작하도록 설계되었다는 것이다.
반대로 리액트 네이티브의 경우 Javascript bridge 를 가운데에 두고 플랫폼 서비스들과 협력해야해서 계속되는 이벤트 등에서 비용이 크다. 이러한 리액트 네이티브 구동방식 및 단점들은 정리된 블로그가 많아서 링크만 남긴다.
모든 것이 위젯
플러터는 모든 것이 위젯이며 위젯의 조합으로 UI를 구성한다. 플러터에 다른 객체가 없다는 뜻이 아니고, 앱을 구성하는 모든 구성들이 위젯 혹은 위젯으로 조합된 위젯이라는 뜻에서 ‘모든 것이 위젯’이라는 뜻이다.
여기서 ‘조합’을 잘 기억해야하는 것이, 플러터에서는 기본적으로 ‘상속’이 아닌 ‘조합’을 통해서 위젯을 구성한다. 예를 들어 Button 으로서 공통 기능, 커스텀 기능이 둘 다 필요한 경우에 일반적으로 객체 지향 방식으로 공통되는 부모 Button 을 만들고 이를 상속받아서 커스텀 Button 을 만드는게 아니라 커스텀 Button 에 공통 Button 을 ‘조합’해서 구현해야 한다.
StatelessWidget vs StatefulWidget
StatelessWidget
StatelessWidget 은 프레임워크에 그 어떤 것도 알리지 않는다. 프레임워크에서 위젯에 언제 리빌드 해야하는지 알려준다. 철저하게 외부(=프레임워크)에 의해서 생명이 결정(‘생명이 결정’ 된다는 말은 위젯의 생명주기가 수동적으로 발생한다는 의미이다.)된다.
수동적으로 철저히 정의된 기능을 수행한다. 즉, 상태가 없는 위젯으로서 새로운 정보에 반응(react)한다.
StatefulWidget
StatefulWidget 은 항상 State 객체를 갖는다. State 객체는 setState()란는 메서드를 갖고 있는데, 위젯을 다시 그려야함을 플러터에 알리는 기능을 수행한다. 이 포인트에서 StatelessWidget 와 크게 구별된다. StatelessWidget 는 프레임워크에 의사표현을 할 수 없는데 반해, StatefulWidget 는 언제 위젯을 다시 그려야하는지에 대해서 프레임워크에 위젯이 발언권을 가지고 있는 것이다.
setState() 이 발생할 경우 해당 위젯 뿐만 아니라 해당 위젯에 의존하는 모든 위젯을 다시 그려야한다고 프레임워크에 지시한다.
StatefulWidget 위젯 생명 주기
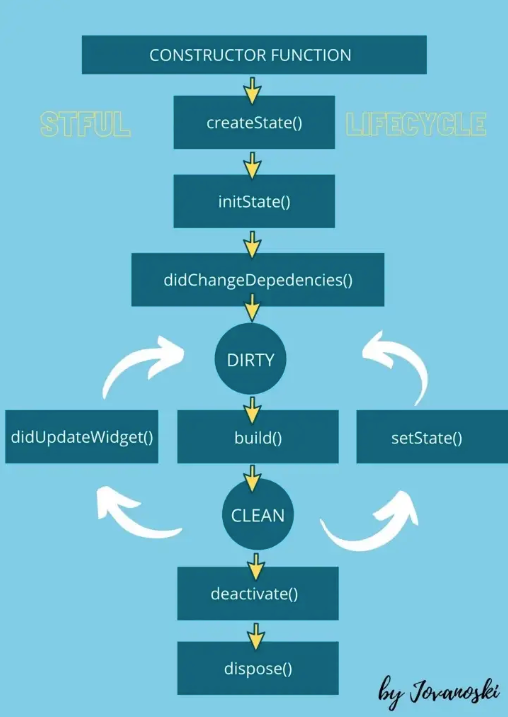
출처: https://betterprogramming.pub/stateful-widget-lifecycle-a01c44dc89b0
StatefulWidget 위젯 생명 주기 이미지 출처이기도 한 포스팅에 아주 자세히 각 생명주기 메서드에 대해 정리가 되어 있다. 이 중 didUpdateWidget(), setState() 이 같은 계층에 있어 조금 더 확실하게 구분 해두면 좋을 것 같아서 따로 아래에 적어둔다.
didUpdateWidget() Gets called if the parent widget changes its configuration and has to rebuild the widget. The framework gives you the old widget as an argument that you can use to compare it with the new widget. Flutter will call the build() method after it. Tip: Use this method if you need to compare the new widget to the old one.
setState() This method is often called from the Flutter framework itself and from the developer. The setState() method notifies the framework that the internal state of the current object is “dirty”, which means that it has been changed in a way that might impact the UI. After this notification, the framework will call the build() method to update and rebuild a widget. Tip: Whenever you change the internal state of a State object, make that change in the setState() method.
플러터 렌더링 동작 원리
플러터가 위젯을 화면에 렌더링 하기까지 많은 과정을 거친다. 이를 자세히 알아보는 챕터였다. 렌더링 하기까지의 과정은 아래와 같다.
위젯 트리 완성 -> 레이아웃 처리(위에서 아래로 ‘제약’ 전파 -> 아래에서 위로 ‘크기’ 설정) -> 조립 -> Rasterization
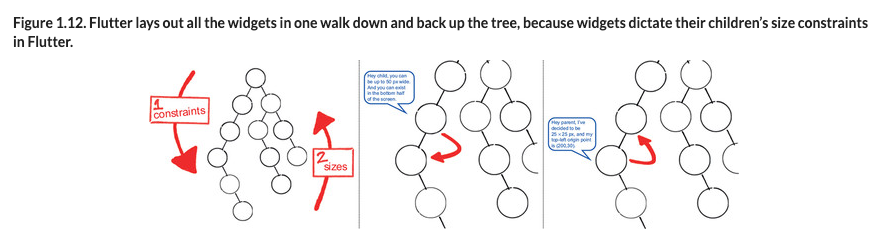
출처 : Flutter In Action
제약 : 자식 노드야. 너는 최대 50px 너비를 가질 수 있고 화면 하단의 절반을 차지할 수 있어.
크기 : 부모 노드님. 저는 25 x 25 px 을 차지하기로 결정했고, 왼쪽 위 시적점은 (200, 30) 이에요.
위젯 트리 완성
화면을 구성하는 위젯들 자체의 정보와 위젯간의 정보가 담긴 위젯 트리를 만든다.
레이아웃 처리(위에서 아래로 ‘제약’ 전파 -> 아래에서 위로 ‘크기’ 설정)
위젯 트리가 완성되면 위에서 아래로(부모에서 자식 방향으로) ‘제약’이 전파된다. ‘제약’이 모두 전파되고 아래에서 위로(자식에서 부모 방향으로) ‘크기’가 전파된다.
조립
위젯 트리 완성 및 레이아웃 처리가 모두 끝나고 바로 래스터라이징하지 않고, ‘조립’의 과정을 거친다. 이 과정에서 위젯은 실제 자신이 처리할 픽셀의 수를 알게 된다. 그리고 이 과정에서 기존의 컴포넌트를 재사용처리 하게 된다.
Rasterization
Rasterization 단어 자체가 의미하는 그대로의 행위이다. 플러터 자체 렌더링 엔진을 통해서 픽셀을 채우는 과정이다.
Last updated